Infineon and Rohm Advance Schottky Diodes for EVs and Renewables
In today’s power electronics industry, semiconductor technologies must be reinvented to handle higher voltages, reduce energy losses, and improve thermal performance. As a ubiquitous device in all power electronics, Schottky diodes are an integral piece of this equation.
Infineon and ROHM have stepped up to deliver new Schottky diode solutions with higher voltage and higher insulation resistance ratings. The recent innovations improve the technical Schottky diode’s technical parameters.
Infineon’s CoolSiC Schottky diode 2000 V G5. Adapted from images used courtesy of Canva and Infineon
Infineon’s 2000 V Schottky Diode
In industrial and renewable energy systems, the DC link functions as an energy buffer between the rectifier and inverter stages as temporary energy storage. The DC link helps reduce losses in power converters by increasing the DC link voltage, which results in a lowered current for a given power level. However, increasing the DC link voltage requires electronic components that can reliably handle this higher voltage level.
One component is the Schottky diode. Compared to general-purpose diodes, Schottky diodes offer uniquely low forward voltage drops and high switching speeds but lag behind in terms of reverse breakdown voltage.
Infineon’s CoolSiC Schottky diode 2000 V G5 is a new solution tailored specifically for DC link systems operating at voltages up to 1500 VDC and up to 80 A. Its silicon carbide (SiC) architecture allows minimal forward voltage drop and eliminates reverse recovery currents, resulting in lower switching losses and enhanced system efficiency.
Architecturally, the diode is designed in a TO-247PLUS-4-HCC package with enhanced creepage (14 mm) and clearance (5.4 mm) distances to guarantee robust insulation in high-voltage environments. The device also incorporates XT interconnection technology, which optimizes thermal resistance and impedance for effective heat dissipation.
ROHM’s High-Insulation SiC Schottky Diodes
In an IC package, creepage distance and insulation resistance are major factors for ensuring reliable operation under high-voltage conditions. While creepage distance measures the path along the surface of an insulator between conductive parts, an IC’s insulation resistance is the resistance offered by its insulating materials to the flow of leakage current between conductive elements under an applied voltage. A longer creepage distance reduces the risk of surface tracking and leakage currents across an insulating surface, improving the insulation resistance of the package under high-voltage conditions.
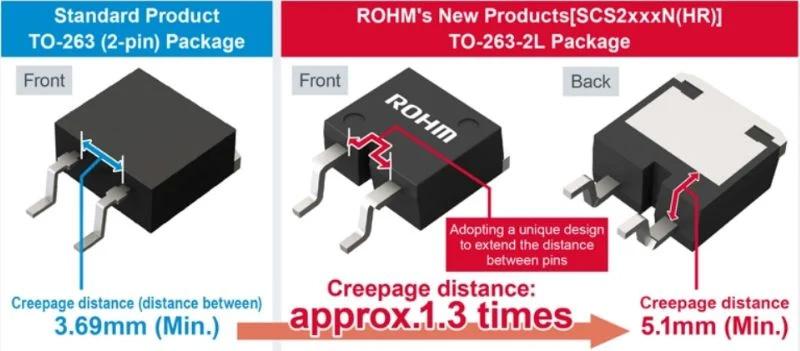
Comparing old and new packages. Image used courtesy of ROHM
The ROHM SiC Schottky barrier diodes feature a package designed with an optimized surface-mount package, enabling an extended creepage distance of 5.1 mm, approximately 1.3 times greater than standard products. By removing the center pin from the bottom of the package, the design minimizes tracking risks and eliminates the need for resin potting.
Furthermore, the diodes offer 650 V and 1200 V breakdown voltage ratings, making them compatible with 400 V automotive and higher-voltage industrial systems. The automotive-grade SCS2xxxxNHR models are qualified to AEC-Q101 standards and are currently in production, while the industrial variants were released in December.
Schottky Diodes and the Future of Power Electronics
As industries increasingly rely on high-efficiency power conversion, such targeted improvements in Schottky diode technology will help unlock more sophisticated, energy-conscious electronic systems.
Sign up to our newsletter
Receive our latest updates about our products & promotions
